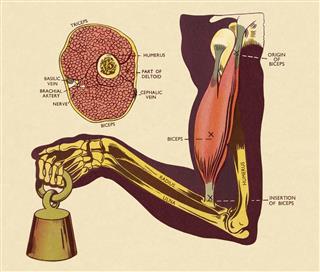
Wondering which is the strongest muscle in the human body, from the huge number of more than 600 muscles present? Well, the answer is not a straight forward one. Just as no organ can be singled out as the most important organ, we cannot single out a particular muscle as the strongest muscle in the human body.
The human body is a unique and intelligently designed structure, with a complex network of muscles enveloping it. Muscles form about 40% of the total body weight. They are contractile tissues, that are formed from the mesodermal layer of the embryonic germ cells.
The various movements we make with our bodies like walking, talking, lifting, smiling, shivering, etc. are all controlled by the different muscles of the body. Besides bringing about movement, the muscles are also responsible for heat generation and maintaining posture. The uniqueness about muscles is that they never stop working. Even while sleeping, the muscles are contracting to maintain posture. They only stop completely when a person is unconscious, and that’s when the body is said to be in a state of complete rest. However, the question here is which is the strongest muscle in the human body. There is a lot of debate over strongest muscle with respective to force, weight, or size. Let us find a definite answer to the question.
Which is the Strongest Muscle in the Body?
The human body comprises over 630 muscles, and to narrow down on the strongest one is not an easy task. This is because each muscle is different in its own way, and cannot be compared on common ground. Some muscles are present individually and some form a group of muscles. Then again some muscles are present in different parts of the body, while muscles like the cardiac muscles are restricted to the heart. So on what basis do we measure the strength?
There is a lot of debate on which is the strongest muscle in the human body. While some title the ‘masseter’ (jaw muscle) to be the strongest muscle, others say the tongue is the strongest muscle. Moreover, muscles like gluteus maximus, external muscles of the eye, heart muscles, uterine muscles and gastrocnemius muscle, are also competing for the strongest muscle title. So who’s the winner?
The problem with strength is that it there is no single platform to measure total strength. Strength can be measured based on different parameters, such as maximum force (absolute maximum strength), repeated motion (dynamic strength), exertion of force quickly (elastic strength), ability to withstand fatigue (strength endurance), etc. Different muscles in the body rate differently based on these parameters. Let’s find out how different muscles rank based on these parameters.
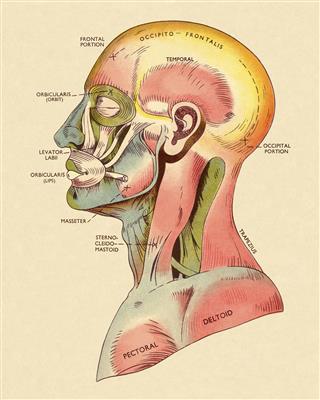
Strongest Muscle Relative to its Strength: Jaw Muscle/Masseter

If the muscle that is able to exert maximum force on an external object is said to be the strongest muscle, then the jaw muscle/masseter can be titled as the strongest muscle in the human body. The masseter works against a shorter lever arm compared to other muscles, and generates the most externally measurable force than any other single muscle can generate.
The jaw muscle lifts the lower jaw, so as to close the mouth while chewing. The multipennate arrangement of fibers gives it the strength for this. The masseter entered the Guinness Book of Records in 1992, as the strongest muscle with an achievement of a bite strength of 4,337 N for 2 seconds.
Strongest Muscle Relative to its Force: Gastrocnemius muscle

Force is another parameter that can help determine the strongest muscle of the body. The muscle that pulls with the greatest force is the gastrocnemius. Along with the soleus muscle, this gastrocnemius muscle forms the calf muscles in the legs.
These muscles help us push our body forward, thereby helping us walk, run, dance, etc. These muscles are the contenders for the strongest muscle relative to their force, as they keep the body upright against the force of gravity. These muscles also prevent people from falling backwards.
Strongest Muscle Relative to its Weight: Muscles of the Uterus

Another parameter that can be considered is the ‘pound for pound’ or weight exerted by a shorter muscle compared to a longer muscle. This parameter makes the myometrial layer of the uterus, a strong muscle. This achievement is based on the ability of the uterus that weighs only 1.1 kg (40 oz) to deliver an infant. This 1.1 kg uterus can exert a force of 100 to 400 N of downward force with each contraction.
Some argue that even though the contraction and relaxation of the uterine muscles, result in childbirth, the muscles do not work on their own, instead have hormonal support during childbirth. So it’s not technically correct to term the muscle as exceptionally strong. Nevertheless, during delivery, the uterus exerts a force of about 100-400N with each contraction.
Strongest Muscle Relative to its Size and Weight: Eye

The extraocular muscles of the eye may sure be small in size, however, their ability to carryout repeated motions is worth noting. When compared to their size and weight, these muscles are said to be ‘100 times stronger than they need to be’. They are also referred to as the ‘busiest’ muscles.
While reading a book, eye muscles make over 10,000 coordinated movements. They also constantly adjust the position of the eye and can fix the eye vision to a steady point. When we are asleep, the eye muscles exercise themselves by carrying out rapid eye movement to be ready for a stressful and straining day ahead.
Strongest Muscle Relative to its Power: Heart

According to some experts, the heart is the strongest muscle, because it works without stopping, irrespective of the stress or trauma the body endures. The heart muscles work continuously to keep us alive, and pumps 2 ounces of blood with every heartbeat. It also pumps about 2,500 gallons (9,450 liters) of blood throughout the day.
The heart can exert a power output of about 1 to 5 watts. The power output of the heart is less compared to other muscles of the body. But this power output is continuous for life without a single pause. This makes the heart the strongest muscle, relative to its power output.
Strongest Muscle Relative to its Size: Gluteus Maximus and Tongue

The largest muscle in the human body is the gluteus maximus or quadriceps femoris, found in the front and sides of the thigh. It is a powerful muscle that helps keep the upper body upright. If there is not enough strength in the gluteus maximus, it may cause people to slump forward or list to one side instead of standing straight. This makes the gluteus maximus the strongest muscle relative to its size.

Another contender in this category is the tongue. The tongue is made up of groups of muscles (16), and is the most flexible muscle. The tongue helps push food down the esophagus, helps talking, etc. Even in ones sleep, the tongue is busy pushing saliva down the throat. It also contains lingual tonsils, at the posterior region that help keep out microorganisms.
Types of Muscles
~ The body comprises three types of muscles; smooth muscles, skeletal muscles and cardiac muscles. The smooth muscles are involuntary muscles, whose movement we cannot control. They make up the walls of the blood vessels, uterus, intestines, internal muscles of the eye, etc.
~ Skeletal muscles on the other hand are those muscles that are connected to the skeletal system of the human body. These muscles are present near the bones and the areas of the skin like the facial muscles. The skeletal muscle contraction helps in movement of the limbs and other parts of the body. Thus, they are voluntary muscles and are in our control.
~ The cardiac muscles as the name suggests are muscles of the heart. They are a type of smooth muscles, and are involuntary muscles. These cardiac muscles make up the walls of the heart. They carry out the function of contraction and relaxation of the heart, for pumping blood throughout the body.
Those were a few parameters that help determine the strongest muscle in the human body. As you can see, a particular muscle cannot be crowned as the strongest muscle. Each muscle performs a different set of important functions to help the body function as one unit. Thus, the human body is made up of a combination of strong muscles!