The human body is one complex network, universally accepted as the most intriguing construct. It is certainly the most widely studied structure the world over. Undermentioned are little- and well-known facts about the human body.
A vast array of aspects concerning the human body have been comprehended; however, there are facets that await a treatment for thorough analysis. The head, neck, torso, a pair of arms and legs, respectively constitute the external view of the body, often described as the superficial, first-layer of the human body. However, internally, the structure is far complex and intricate. Know that there are 11 organ systems of the body: Circulatory System, Respiratory System, Immune System, Skeletal System, Excretory System, Urinary System, Muscular System, Endocrine System, Digestive System, Nervous System, and Reproductive System.
INDEX
● Parts of the Body
● Organs of the Body
● You Can Live Without …
● Body-double Foods
● Practice Diagrams

Head
The human head consists of the brain, a pair of eyes and ears, a nose and mouth, all of which help in various sensory functions, such as the ability to process thought, see, hear, smell, and taste.
Did You Know…
☛ The human eye has the ability to differentiate between 400+ shades of gray, and what’s more, it can identify approximately 10 million colors.
☛ Your ears never sleep. Sound is received even while you are asleep; it’s the brain that does not process them.
☛ Our noses and ears continue to grow because of gravity (starts to droop/sag) and cartilage (which continues to grow as we age).
☛ Your taste buds are not only present on your tongue; the palate and your throat passage, have taste buds too.
☛ Every day, the number of thoughts that human beings process are roughly estimated to be 70,000.
Neck
The neck is the junction between the head and the torso. It has been derived from the Latin word “cervical” which means “of the neck.” Our spinal cord has 33 small bones, which are called the vertebrae. Out of the 33, 7 bones are located in the neck region, known as the cervical curve.
Did You Know …
☛ A free bone, indeed; the hyoid bone (lingual bone) located below the Adam’s apple, is the only bone not attached to the human skeleton.
Torso
The human torso is also known as the ‘trunk’. It is the central part of the body, and it is from here that the neck and the limbs extend. Some of the most critical human body organs are situated within the torso. The upper part consists of the heart and the lungs; these are protected by the rib cage. The middle region or the abdominal area consists mainly of organs which help in digestion. It has the liver, the large and the small intestine, the anus from where fecal waste is excreted, and the rectum where the feces is stored.
Then you have the gallbladder which stores bile produced by the liver, and concentrates it to produce chyme. Then there is the ureter, from where urine is passed to the urinary bladder and stored; the urethra expels urine. Finally, comes the third part of the torso, the pelvic region. This has the male and female reproductive organs. The torso of the human body also consists of the major muscles of our body; the pectoral muscles, the abdominal muscles, and the lateral muscle.
Did You Know…
☛ While the size of the human head right from birth won’t change drastically, it is the torso and the lower limbs that grow in length.
Arms
Of the two pairs of limbs that we have, our arms form the upper limbs, also known as forelimbs. In anatomical terms, the word ‘arms’ indicates the segment between the shoulder and the elbow, while ‘forearm’ is the segment between the elbow and the wrist. However, the term commonly refers to the entire limb, starting from the shoulder to the wrist. The arms help us perform a variety of tasks in a day.
Did You Know…
☛ When you wave your wrist, all the bones of your arm are at work.
Legs
The legs are also known as the lower limbs, and they help us bear the weight of the entire body besides facilitating movement.
Did You Know…
☛ The femur bone, also known as the thigh bone, is the longest bone in the body. It is deemed far stronger than concrete!

Brain
The brain aids us to think, comprehend, and create. Marked by folds that meander through the surface area of the brain, the signals in the form of information, are passed from the brain as they navigate through the spinal cord, and then transported to other parts of the body. Know that the brain has four sections: the cerebrum, cerebellum, diencephalon, and brain stem.
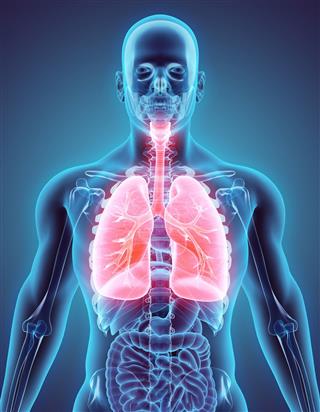
Lungs
Regarded as the most vital organ of the respiratory system, a pair of lungs is located inside the chest, their primary function being the release of oxygen into the blood and extricating carbon dioxide from the blood. The trachea – also known as the windpipe – serves as the passageway for inhalation. When oxygen passes through the trachea into the lungs, it goes through tiny air sacs called alveoli. As oxygen penetrates the alveoli, the carbon dioxide is extricated from the blood as we exhale.
❒ Know This (?)
As astounding as it may sound, the lungs consist of over 300,000 capillaries. If they stretched into a line, placed end to end, the distance they would cover would be approximately 2400 km!
Heart
The heart is the most active muscular organ, residing marginally on the left section of the body that tirelessly supplies blood to the entire system. The heart pumps and circulates blood through the body, following a contraction-relaxation cycle. Blood is carried throughout the body through the capillaries, while the coronary arteries supply blood to the heart.
❒ Know This (?)
The heart can beat all by itself even after being separated from the body. The heart possesses its own electric impulse that causes it to function without the body, provided that it receives a constant supply of oxygen.
Liver
An important organ of the digestive system, the liver is located below the diaphragm and to the right of the stomach. The major function of the liver is to process and store substances ingested through the mouth, and those that we inhale and absorb via the epidermal layers. It essays an essential role in extricating matter that can be potentially toxic.
❒ Know This (?)
The liver is a very hardworking organ that filters more than a liter of blood per minute.
Stomach
The stomach is another vital organ of the digestive system. The substances ingested will pass the esophagus and lead its way into the stomach. The stomach stores food for a short period while the lining releases hydrochloric acid to facilitate the break down of food. The digestive acid it secretes is very strong and thus kills the bacteria that may cause damage to the lining of the stomach. It is protected from the harmful effects of the acid, by a mucosal substance that lines the abdominal cavity. The process reduces solid food into soft, mush-like matter which is then transported to the small intestine, that continues the process of digestion.
❒ Know This (?)
A new stomach lining is formed within a period of three to four days. Why? Well, know that the digestive acids produced in the stomach are so strong, that they might as well burn a hole, quite literally, through your stomach wall.
Spleen
The spleen is an organ that helps fight infection and balances bodily fluids. It cleanses the blood of bacteria and other harmful substances that may pose a threat to the smooth functioning of the entire system. The spleen also functions as the exterminator of toxicities along with unhealthy red blood cells.
❒ Know This (?)
In Ancient Greece, it was believed that the body consisted of fluids that may adversely affect an individual’s mood. The spleen was held responsible for making people feel sad or what was known as melancholia. It was believed that the spleen produced a black-colored fluid which interfered with the normal functioning of the system.
Pancreas
The pancreas is an organ located above the small intestine. It secretes digestive juices into the duodenum and aids in efficient digestion. Besides, it also controls sugar levels in the blood.
❒ Know This (?)
Researchers suggest that the pancreas consists of taste receptors that can identify sweet substances.
Gallbladder
The gallbladder resides under the liver and collects bile produced in the liver. It releases the bile after extracting water content from it into the small intestine, to facilitate the breakdown of fat and protein ingested through the food we consume.
❒ Know This (?)
The gallbladder mimics the mechanism of a balloon. Before a meal, the gallbladder enlarges itself with bile. The bile is released into the small intestine to digest fat and protein; this extraction of bile leads the gallbladder to deflate.
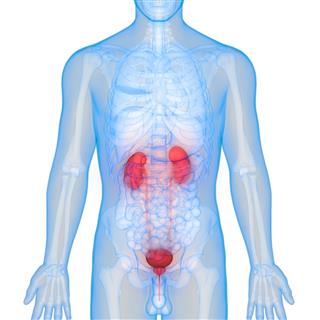
Kidney
Located toward the rear of the body, the kidneys are a pair of organs that cleanse blood and regulate water levels in the body. The primary function of the kidney is to extract water accompanied with other constituents from the blood. Waste matter is extricated from the system in the form of urine. Besides, the kidneys are also responsible for filtering blood and regulating blood pressure.
❒ Know This (?)
Healthy kidneys work toward filtering approximately two gallons of blood every hour.
Bladder
The bladder holds liquid waste matter — the urine. When the bladder starts to inflate, it triggers a signal to the brain indicating that its capacity is exhausted, and it needs to be relieved. The urine travels from the bladder through a tube called the urethra to be extricated from the body.
❒ Know This (?)
The urethra of a female’s is shorter, i.e., approximately 2.5 cm; whereas, in men, the passage is approximately 15 cm.
Small Intestine
The small intestine is a coiled organ where food passes through, beginning from the duodenum where the food intermixes with bile to facilitate the break down of fat and protein. The intestine is lined with microvilli; they are tiny projections that help in the absorption of nutrients from the food ingested.
❒ Know This (?)
The length of the small intestine is 18 to 23 feet, and is longer than the large intestine. It’s diametrically smaller than the large intestine; this is precisely the reason why the small intestine is regarded as “small.”
Large Intestine
The large intestine constitutes the cecum and the colon. As the break down of food is a process conducted in the small intestine, the role of the large intestine is to absorb water and minerals, and process the remains of the digested food into fecal matter.
❒ Know This (?)
The large intestine houses more than 700 species of bacteria. They are a source of vitamins and are deemed essential for the body.
Appendix
The appendix is a small, finger-like structure, attached to the large intestine. Thought to be useless, it is an organ much speculated for its role in the human body.
❒ Know This (?)
As mentioned, the appendix performs no apparent function in the human body. However, researchers are of the opinion that the appendix is a rather useful organ to deal with certain issues, with regard to digestion. Besides, researchers suspect that the appendix may save you from pernicious infections as well.
Uterus and Ovaries
The uterus – also known as the womb – is a pear-shaped organ. The cervix forms the lower section of the uterus, that opens into the vagina. The other major section of the uterus is regarded as the corpus, and serves as an expandable vessel that has the capacity to hold a growing fetus. The uterus has two oval-shaped glands on either of its sides, known as the ovaries.
❒ Know This (?)
The uterus is 2 to 3 cm thick, while in length it is 6 to 8 cm, approximately.
Testes and Penis
The testes is the male gonad; this being a part of the reproductive system. The function of the testes is to produce sperm and testosterone. The penis is a sexual organ, functioning as the passageway to pass urine and ejaculate
semen.
❒ Know This (?)
If the testes ache or have a dull pain in the vicinity, it is due to the prostate swelling with excess fluid. This is known as prostatic congestion.
Arranged here are ten body parts that surprisingly, you can live without.
The human body is marked by its structural complexity, and maintaining health with the right foods is of paramount importance. However, besides eating right, it’s eating smart that gains a stronger foothold in the health department. It is found that there are certain foods that share an uncanny resemblance with the parts of the human body, thereby deemed effective in maintaining the specific part of the body, too. Thus, in order to keep your body and mind healthy, undermentioned are foods that help maintain them.
Walnuts ⇆ Brain
Now this nut is a give away for sure. Walnuts, pound for pound, resemble the human brain. The folds and crevices, too, of the brain are mimicked perfectly by nature. Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, regular consumption of this nut facilitates the functions of the brain.
Carrots ⇆ Eyes
Health care providers perpetually recommend to nibble on carrots to keep your eyes healthy and active. Besides its befitting benefits, you must notice the radial pattern when the carrot is sliced diametrically. Get closer, and you are sure to find a striking resemblance between the human eye and the carrot slice. The pattern created looks like the pupil and iris. The most important component — beta-carotene — is potent in reducing the risk of cataracts.
Mushroom ⇆ Ears
Slice open a mushroom, and you’ll that it looks like the ears. You must know that mushrooms contain vitamin D in abundance which is deemed essential for effective hearing. Vitamin D is also essential in maintaining bone health in the ears, which include the malleus, incus, and strapes that aid in receiving sounds and transmitting the same to the brain.
Orange ⇆ Breasts
The relation between oranges and breasts may go well beyond the obvious factor of resemblance. Oranges and grapefruits, too, maintain breast health and facilitate the movement of lymph in the breasts. Besides, grapefruits have a component called limonoids that help in reducing the risk of developing breast cancer.
Tomato ⇆ Heart
Tomatoes look like the heart. It is red; and when sliced into halves, it generally has four chambers — characteristics that resemble the heart. Tomatoes are known to be high in lycopene — a plant chemical that protects the heart and reduces its risks of succumbing to a cardiac arrest.
Ginger ⇆ Stomach
Ginger root is one spice that more or less resembles the stomach. Besides being added to enhance flavors of your dish, ginger also aids in effective digestion.
Kidney Beans ⇆ Kidneys
There is no doubt that kidney beans look like kidneys. They help to facilitate the smooth functioning of the kidneys.
Sweet Potato ⇆ Pancreas
A look at the sweet potato and it tells you what it’s meant for. Bearing resemblance to the pancreas, sweet potatoes are rich in beta-carotene that helps prevent the adverse effects of aging on the tissues of the body. Besides, it is also known to maintain one’s glycemic index, thus aiding those with diabetes.
Celery ⇆ Bones
Celery is one food that concentrates on bone density. Bones are known to consist of 23% sodium and coincidentally celery, too, contains 23% sodium.
Avocados ⇆ Uterus
Avocados along with pears, have an appearance that is strikingly similar to the womb and cervix of the female body. Besides, it corrects hormone imbalance and reduces the risk of succumbing to cervical cancer.
Clams ⇆ Testes
Rich in zinc and folic acid, clams resemble the testicles. It is known to improve the quality of semen in men.
These diagrams help you learn the basics and understand the human body better. Click on the images if you wish to have them printed.