The endocrine system consists of glands that are found all over the body, which help you to produce hormones. This article provides detailed information about the endocrine system.
The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete various chemicals called hormones. These are messages that pass signals through the blood to a targeted organ. The receptor cells recognize these messages and act accordingly. Hormones are divided into three classes based on their structure:
- Steroids
- Peptides
- Amines
The steroid hormones are derived from cholesterol after a series of biochemical reactions. They pass through the bloodstream, and are not stored by cells. The production of this hormone depends on the rate of synthesis. The peptide hormones are synthesized as precursor molecules. Endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi bodies process these chemicals that are stored in secretory granules, which further help in their secretion into the blood stream, as and when the body demands it. The amine hormones are stored in the cytoplasm as granules till needed.
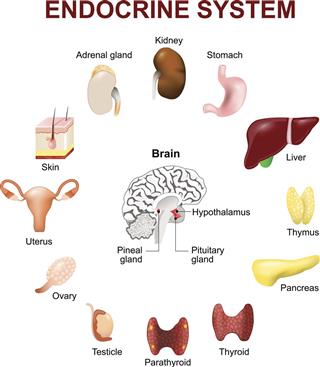
Endocrine System Organs
There are over 20 major hormones that are pumped into the bloodstream directly by the endocrine system glands. This system organs consists of the following glands in human begins:
- Hypothalamus
- Pituitary Gland
- Pineal Gland
- Thyroid Gland
- Parathyroid Glands
- Adrenal Glands
- Islets of Langerhans (Pancreas)
- Ovaries (Females)
- Testes (Male)
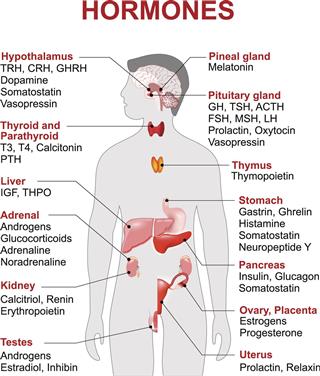
Endocrine System Functions
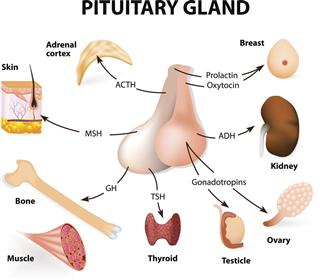
Pituitary gland
Antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin)
Helps the kidneys to retain water, and controls blood pressure in the presence of aldosterone.
Corticotropin (ACTH)
Controls production and secretion of hormones of the adrenal glands.
Human growth hormone
Regulates growth and development, and promotes protein production.
Luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormone
Controls reproductive functions that includes the production of sperm and semen, egg maturation, and menstruation. It also regulates male and female sexual characteristics that includes hair distribution, muscle formation, skin texture and thickness, voice, and may even control personality traits.
Oxytocin
It causes muscles of the uterus and milk ducts in the breasts to contract.
Prolactin
It starts and maintains milk production in the mammary glands.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
It controls the stimulation, production, and secretion of hormones of the thyroid gland.
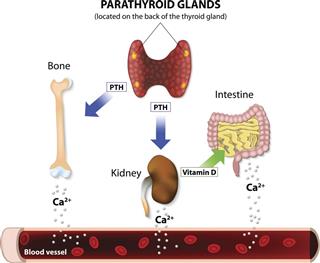
Parathyroid glands
Parathyroid hormone
It regulates the formation of bones and excretion of calcium and phosphorus.
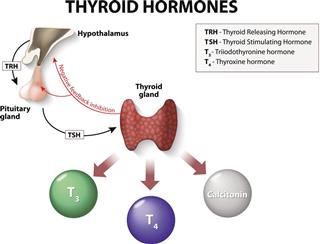
Thyroid gland
Thyroid hormone
It regulates the body’s metabolic rate.
Calcitonin
Its function is still unclear, but in other species, it regulates calcium balance.
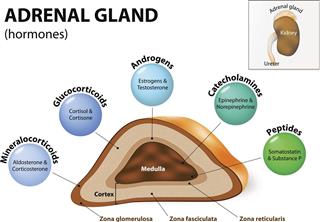
Adrenal glands
Aldosterone
It helps in regulation of salt and water balance by their retention and excretion of potassium.
Cortisol
It has widespread effects in the whole body. It mainly causes anti-inflammatory action, maintaining blood sugar level, blood pressure, and muscle strength. It also helps to control salt and water balance.
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)
It affects the bones, mood, and the immune system
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
This chemical stimulates the heart, lungs, blood vessels, and nervous system.
Pancreas
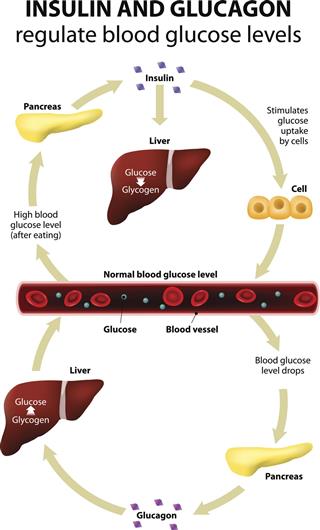
Glucagon
It helps in raising the blood sugar level.
Insulin
This chemical helps in lowering the blood sugar level, and affects the metabolism of sugar, protein, and fat throughout the body.
Kidneys
Erythropoietin
Stimulates red blood cell production.
Renin
It controls blood pressure.
Ovaries
Estrogen
It helps in the development of female sex characteristics and the reproductive system.
Progesterone
Prepares the lining of the uterus for implantation of a fertilized egg, and readies the mammary glands to secrete milk.
Testes
Testosterone
It controls the development of sexual characteristics in men and the reproductive system.
Digestive tract
Cholecystokinin
It controls the gallbladder contractions that cause the bile to enter the intestine, and stimulates release of digestive enzymes from the pancreas.
Glucagon-like peptide
This chemical increases the releasing of insulin from the pancreas.
Ghrelin
It controls the growth hormone release from the pituitary gland, and causes a sensation of hunger.
Adipose (fat) tissue
Resistin
It blocks the effects of insulin on muscle.
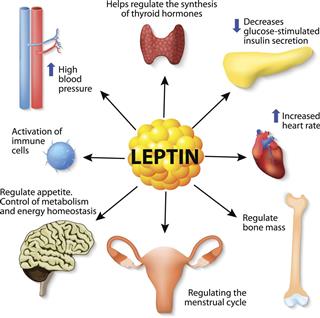
Leptin
This chemical controls appetite.
Placenta
Chorionic gonadotropin
Stimulates the ovaries to continue releasing progesterone during early pregnancy.
Estrogen and progesterone
It helps keep the uterus receptive to the fetus and placenta during pregnancy.
Endocrine System Facts
- There are no ducts in this system. The hormones produced are released directly into the bloodstream, and then carried to various organs.
- There are about 30 different hormones produced by this system, each of which has a distinct function.
- The pineal gland secretes melatonin that regulates sleep.
- Adrenal glands produce adrenaline when one gets excited or frightened.
- If the pancreas fails to regulate insulin production, it will lead to diabetes.
- If you feel hungry and thirsty, it means your hypothalamus is doing its job well.
- The endocrine glands helps the immune system to ward off infections.
- They also affect the nervous system, and lead to many behavioral changes in humans.