The calf muscles bear the body weight to a large extent. Therefore, athletes/sportsmen experience cramps/strain/pull quite often. The following article provides information on these muscles.
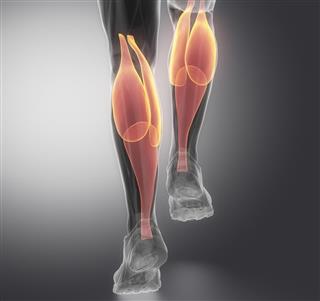
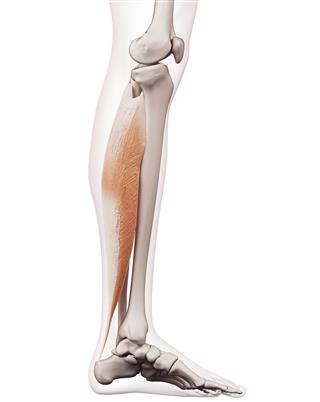
The fleshy hind part of the back of the leg below the knee is called the ‘calf’. Scientifically, this muscle is known as triceps surae. These are a pair of muscles called soleus and gastrocnemius. Both the muscles together converge at the heel bone of the foot. Contraction of the triceps surae induces the movement of plantar flexion. These muscles also provide stability to the ankle complex.
Anatomy
While gastrocnemius is the superficial portion, soleus is the deep mass of muscle. They are explained in detail below:
- Soleus: These muscles lie on the inside of gastrocnemius. This powerful muscle extends from the knee to the heel. It supports the walking and standing activities. This muscle is not present in all the mammal species. For instance: it’s absent in dogs.
- Gastrocnemius: This muscle is located to the anterior of soleus muscle. Owing to its bulging shape, it is also referred to as ‘stomach of leg’. These extend between the knee and the heel. This muscle is attached to the knee by means of two heads, i.e., the lateral and the medial head. These heads originate from the lateral and the medial condyles respectively. Its main function is ankle movement. The muscle is also involved in the movement of knees.
- Plantaris: It is a smaller muscle among the superficial ones. This muscle assists the movements of gastrocnemius and soleus.
The information about the deep muscles of triceps surae region is presented below.
- Flexor Hallicus Longus: The word, hallicus is used with reference to the big toe. Flexor hallicus longus extends from the back portion of the leg until the bottom of the big toe. This muscle enables the movement of bending of the big toe.
- Flexor Digitorm Longus: Its function is similar to that of the flexor hallicus longus, however, flexor digitorm helps in the movement of all toes except the big toe.
- Polpliteus: This muscle controls the smooth movement of the knee at the time of walking.
Grades of Strain
The pain may be caused due to the overworking of these muscles through workouts.
One of the reasons could be improper stretching. Sports persons who participate in games such as soccer, football, rugby, hurdles, long jump, running, etc., are more susceptible to these pains and swelling.
The different conditions associated with this muscle pain are listed below.
- Grade 1 Muscle Strain: Stretching of muscles cause small micro-tearing in the muscle fiber. Full recovery takes at least 2 weeks.
- Grade 2 Muscle Strain: There is partial tearing of muscle fibers. It takes 5 – 8 weeks to fully recover.
- Grade 3 Muscle Strain: This is the most severe of all the three grades. In this condition, the muscle fiber of lower leg is totally ruptured/torn. A period of more than 3 – 4 months is required for full recovery. In some cases, surgery may be required.
- Inflammation: Pain may be caused due to the inflammation of the subcutaneous tissues.
Listed are certain exercises that can strengthen these muscles:
- Skipping: It is one of the best exercises for triceps surae. However, skipping should be performed for not more than 20 minutes at a stretch, otherwise, it may cause sore muscles.
- Squats: Squats are usually practiced to strengthen muscles. Performing 10 – 15 squats with extra weights is effective in strengthening muscles.
Treatment
The R.I.C.E. (rest, ice, compression, and elevation) treatment technique can be used:
- Rest: Avoid impact activity or excessive stretching.
- Ice: Ice needs to be rubbed on the muscle every 2 – 3 hours to relieve the strained muscle
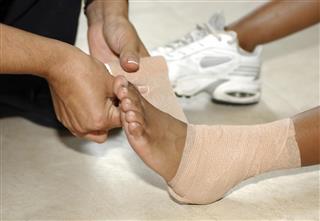
- Compression: Wrapping the injured part with an elastic bandage, prevents blood from pooling in the foot.
- Elevation: The foot needs to be kept elevated to reduce the swelling.
Call for a medical practitioner at the earliest to avoid complications. Sports persons should await full recovery of the torn muscles. If they return to sports too soon, there is a risk of developing a chronic injury. Everyone recovers at a different rate, so ensure you consult the doctor before to resume sports.
Disclaimer: This Bodytomy article is for informative purposes only, and should not be used as a replacement for expert medical advice.