The rib cage protects the organs in the thoracic cavity. An injury to any of these organs can prove to be life-threatening. This Bodytomy article presents a list of the organs that need protection.
There are many cavities in the human body, for example, the cranial cavity in the head, the thoracic cavity, the abdominopelvic body cavity below the thoracic cavity, and the dorsal cavity that covers the backside of the body, etc. Thoracic cavity or the chest cavity is an important chamber in the human body. It is the second largest cavity in the body. The ribs, vertebral column, muscles, connective tissues, and the sternum (breast bone) enclose this cavity.
The thoracic cavity is lined by a serous membrane that exudes a thin fluid (serum). The chest membrane, also known as parietal pleura, extends further to cover the lungs. This part of the membrane is known as the visceral pleura. The part of the membrane that covers the heart, esophagus, and the great vessels is known as mediastinal pleura. Mediastinum refers to the middle space, the space between the lungs that extends from the sternum, back to the vertebral column. Friction between the two adjacent membranes during the process of respiration (as various organs expand and contract) is lowered by the fluid secreted by the serous membrane. The fluid acts as a lubricant.
What are the Thoracic Cavity Organs?
Cardiovascular System
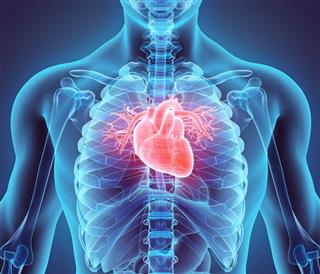
One of the most important part of the human body system is the cardiovascular system. The system consists of the heart and all the great vessels of the heart (the aorta, the pulmonary artery, the pulmonary vein, the superior vena cava, and the inferior vena cava), and the veins in the azygos system.
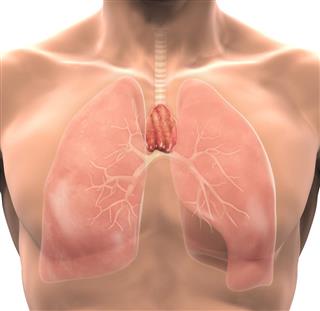
Respiratory System
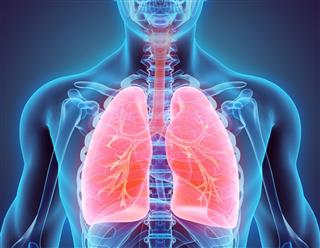
The diaphragm, lungs, trachea, and the bronchi are the main respiratory system organs in the thoracic cavity.
Digestive System
Most of the digestive system organs are located in the abdominal cavity. However, the esophagus, the tube that carries food to the stomach is located in the thoracic cavity.
Endocrine System
The thymus gland (it is more associated with the immune system than the endocrine system), and the thyroid gland are also important organs in the pectoral cavity.
Nervous System
The paired vagus nerves and the paired sympathetic chains are the major nervous system organs present in the chest cavity.
Lymphatic System
The thoracic duct, a part of lymphatic system, is also an important organ. Parietal lymph nodes located in the thoracic wall and visceral lymph nodes that are associated with the internal organs comprise thoracic lymph nodes.
There are empty spaces (cavities) in the thoracic cavity that are lined with mesothelium. These cavities include the two pleural cavities, one pericardial cavity, and the mediastinum. The space between the two pleurae (visceral and parietal) of the lungs is called pleural cavity. The double-walled sac called pericardium contains the heart and the roots of the great vessels. The space between the two layers of pericardium is called the pericardial cavity. As it is filled with a fluid, it protects the heart from external shocks. Thus, even the cavities play an important role in the functioning of the systems and organs.
Various bones such as the ribs, the clavicles, the vertebrae, and sternum help protect the organs in the thoracic cavity, and also support the body. One can safely say that the thoracic cavity is the vault of the human body that contains the most precious organs essential to life.